Business Plan Translation [Korean → English]

The following pages were taken from 40 page long business plan for an organic waste composting facility in Korea.
다음은 한국의 유기성 폐기물 퇴비화 시스템 설비에 대한 40페이지 분량의 사업계획서에서 발췌된 내용입니다.
The document was prepared for the purpose of public sector involvement and securing government grants—first drafted in Korean and translated into English.
해당 문서는 공공 부문 참여 및 정부 보조금 지원 확보를 목적으로 작성되었고, 한글로 우선 작업 후 영문으로 번역하였습니다.
당면과제 및 정책현황
BACKGROUNDS & CHALLENGES
01. 전국 폐기물 발생 및 처리현황
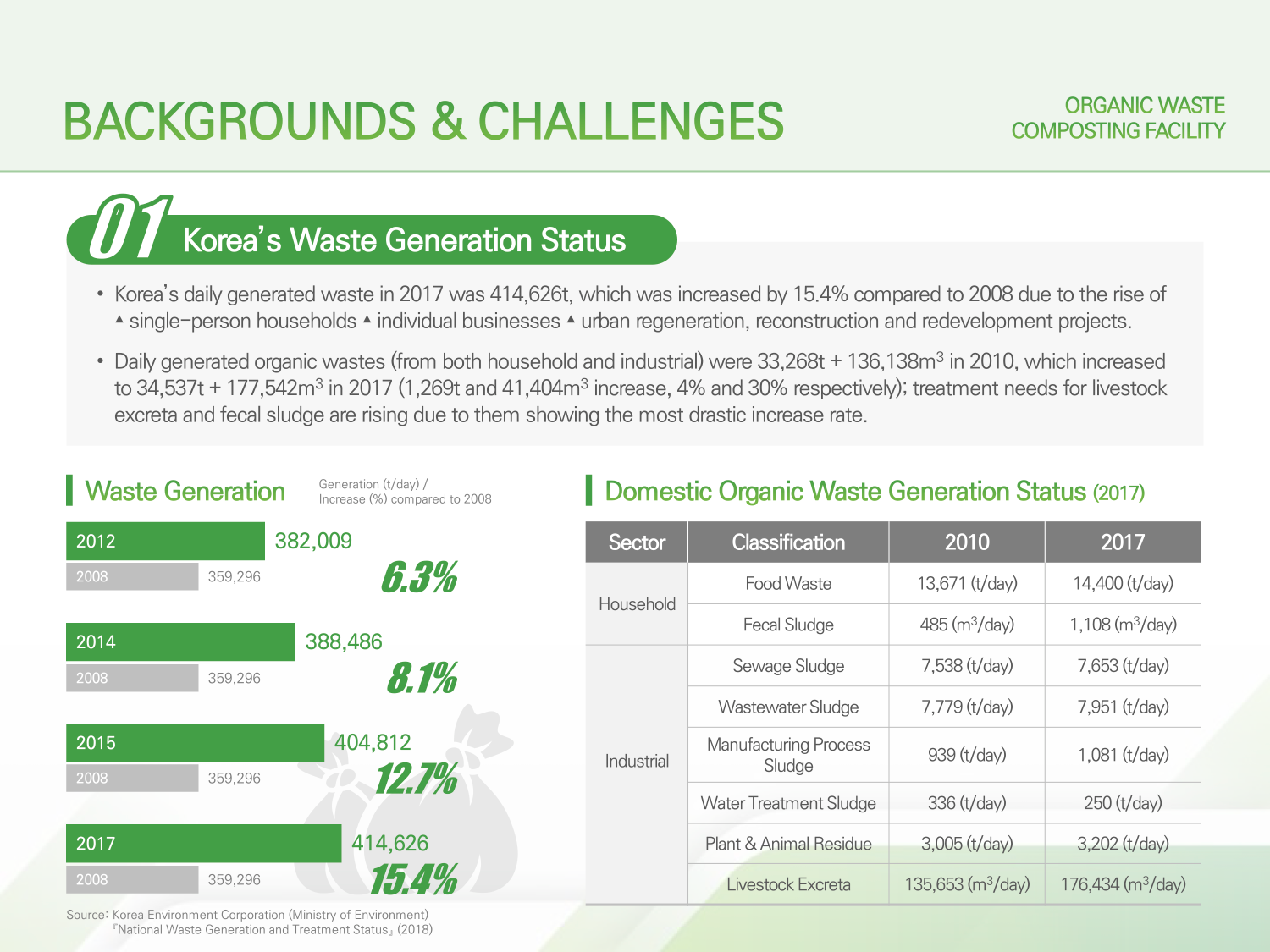
→ 01. Korea’s Waste Generation Status
우리나라의 하루 폐기물 발생량은 2017년 기준 41.4만 톤으로, 이는 10년 전 대비 15.4% 증가한 수치인데 ▴1인 가구 증가 ▴개인사업장 증가 ▴도시재생 및 재건축·재개발 사업 등이 그 원인으로 파악
→ Korea’s daily generated waste in 2017 was 414,626t, which was increased by 15.4% compared to 2008 due to the rise of ▴single-person households ▴individual businesses ▴urban regeneration, reconstruction and redevelopment projects.
가정과 사업장에서 하루 발생하는 유기성 폐기물은 2010년 33,268톤과 136,138㎥이며, 2017년 34,537톤과 177,542㎥로 7년간 1,269톤과 41,404㎥로 각각 약 4%와 30%증가, 가축분뇨와 분뇨처리 오니의 증가폭이 가장 커 처리에 대한 사회적 요구도 상승
→ Daily generated organic wastes (both household and industrial) were 33,268t + 136,138㎥ in 2010, which increased to 34,537t + 177,542㎥ in 2017 (1,269t and 41,404㎥ increase, 4% and 30% respectively); treatment needs for livestock excreta and fecal sludge are rising due to them showing the most drastic increase rate.
02. 역대 최대치 예산안을 편성한 환경부
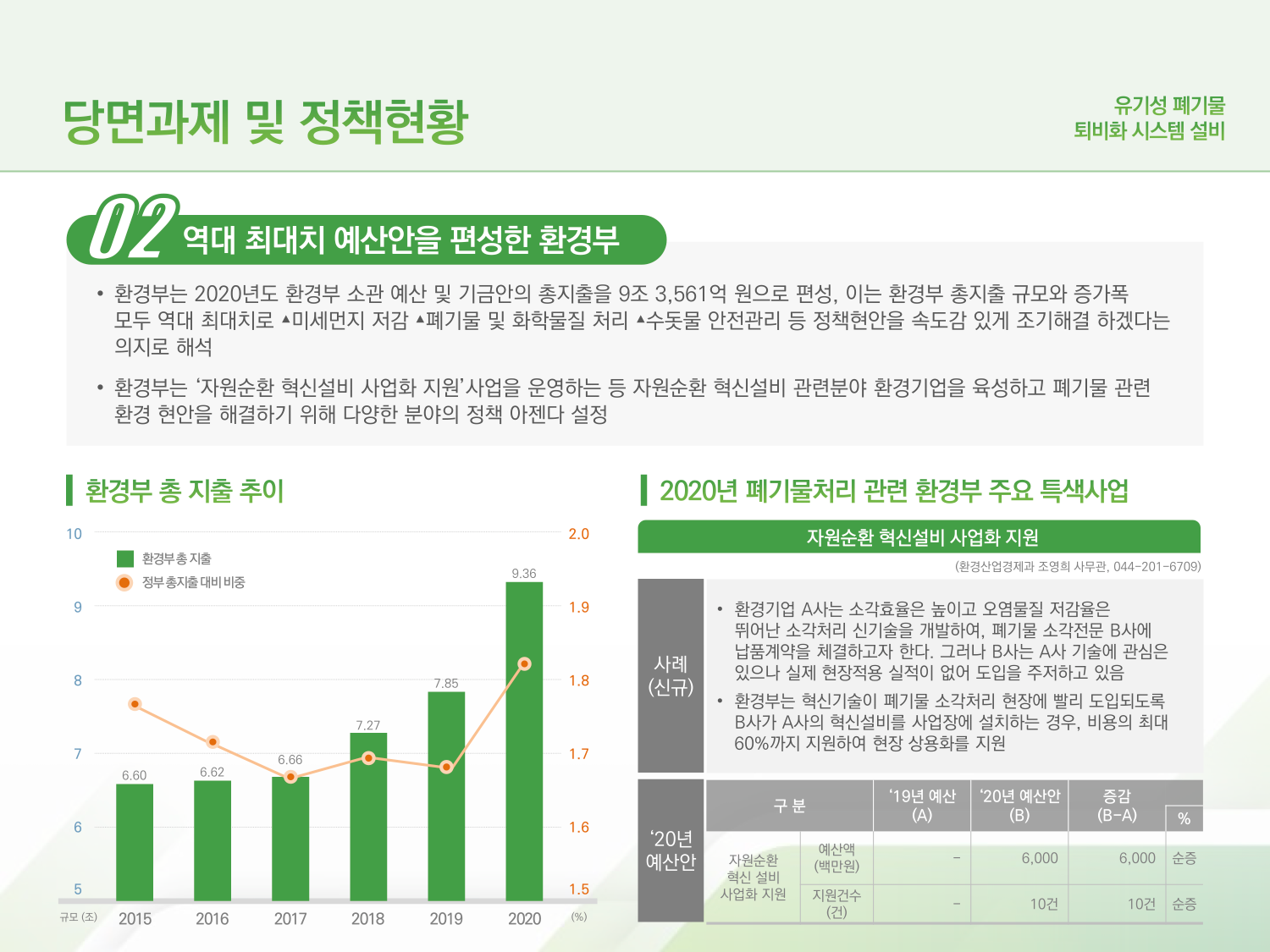
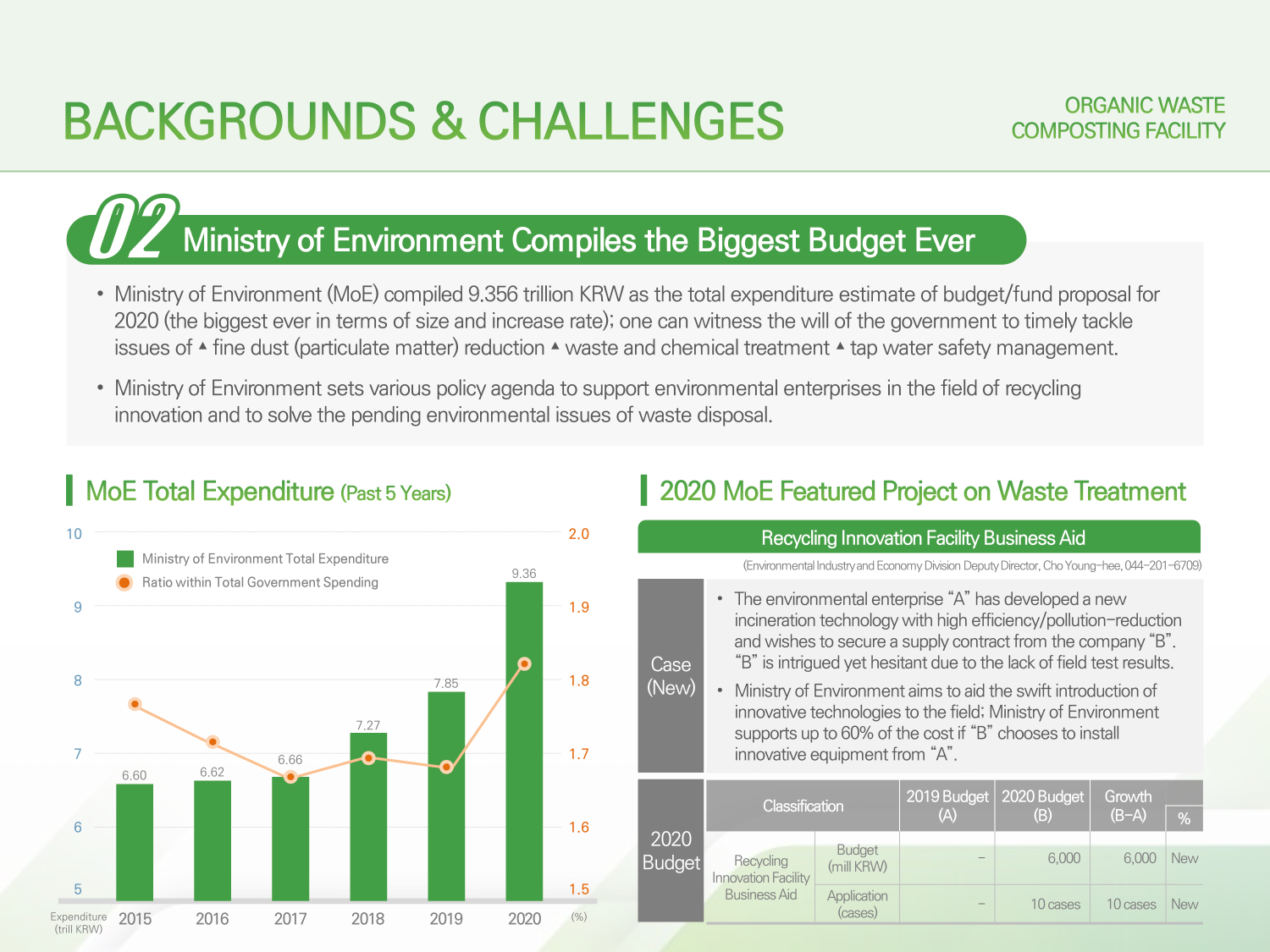
→ 02. Ministry of Environment Compiles the Biggest Budget Ever
환경부는 2020년도 환경부 소관 예산 및 기금안의 총지출을 9조 3,561억 원으로 편성, 이는 환경부 총지출 규모와 증가폭 모두 역대 최대치로 ▴미세먼지 저감 ▴폐기물 및 화학물질 처리 ▴수돗물 안전관리 등 정책현안을 속도감 있게 조기해결 하겠다는 의지로 해석
→ Ministry of Environment (MoE) compiled 9.356 trillion KRW as the total expenditure estimate of budget/fund proposal for 2020 (the biggest ever in terms of size and increase rate); one can witness the will of the government to timely tackle issues of ▴fine dust (particulate matter) reduction ▴waste and chemical treatment ▴tap water safety management.
환경부는 ‘자원순환 혁신설비 사업화 지원’사업을 운영하는 등 자원순환 혁신설비 관련분야 환경기업을 육성하고 폐기물 관련 환경 현안을 해결하기 위해 다양한 분야의 정책 아젠다 설정
→ Ministry of Environment sets various policy agenda to support environmental enterprises in the field of recycling innovation and to solve the pending environmental issues of waste disposal.
2020년 폐기물처리 관련 환경부 주요 특색사업 - 자원순환 혁신설비 사업화 지원
→ 2020 MoE Featured Project on Waste Treatment - Recycling Innovation Facility Business Aid
환경기업 A사는 소각효율은 높이고 오염물질 저감률은 뛰어난 소각처리 신기술을 개발하여, 폐기물 소각전문 B사에 납품계약을 체결하고자 한다. 그러나 B사는 A사 기술에 관심은 있으나 실제 현장적용 실적이 없어 도입을 주저하고 있음.
→ The environmental enterprise “A” has developed a new incineration technology with high efficiency/pollution-reduction and wishes to secure a supply contract from the company “B”. “B” is intrigued yet hesitant due to the lack of field test results.
환경부는 혁신기술이 폐기물 소각처리 현장에 빨리 도입되도록 B사가 A사의 혁신설비를 사업장에 설치하는 경우, 비용의 최대 60%까지 지원하여 현장 상용화를 지원.
→ Ministry of Environment aims to aid the swift introduction of innovative technologies to the field; Ministry of Environment supports up to 60% of the cost if “B” chooses to install innovative equipment from “A”.
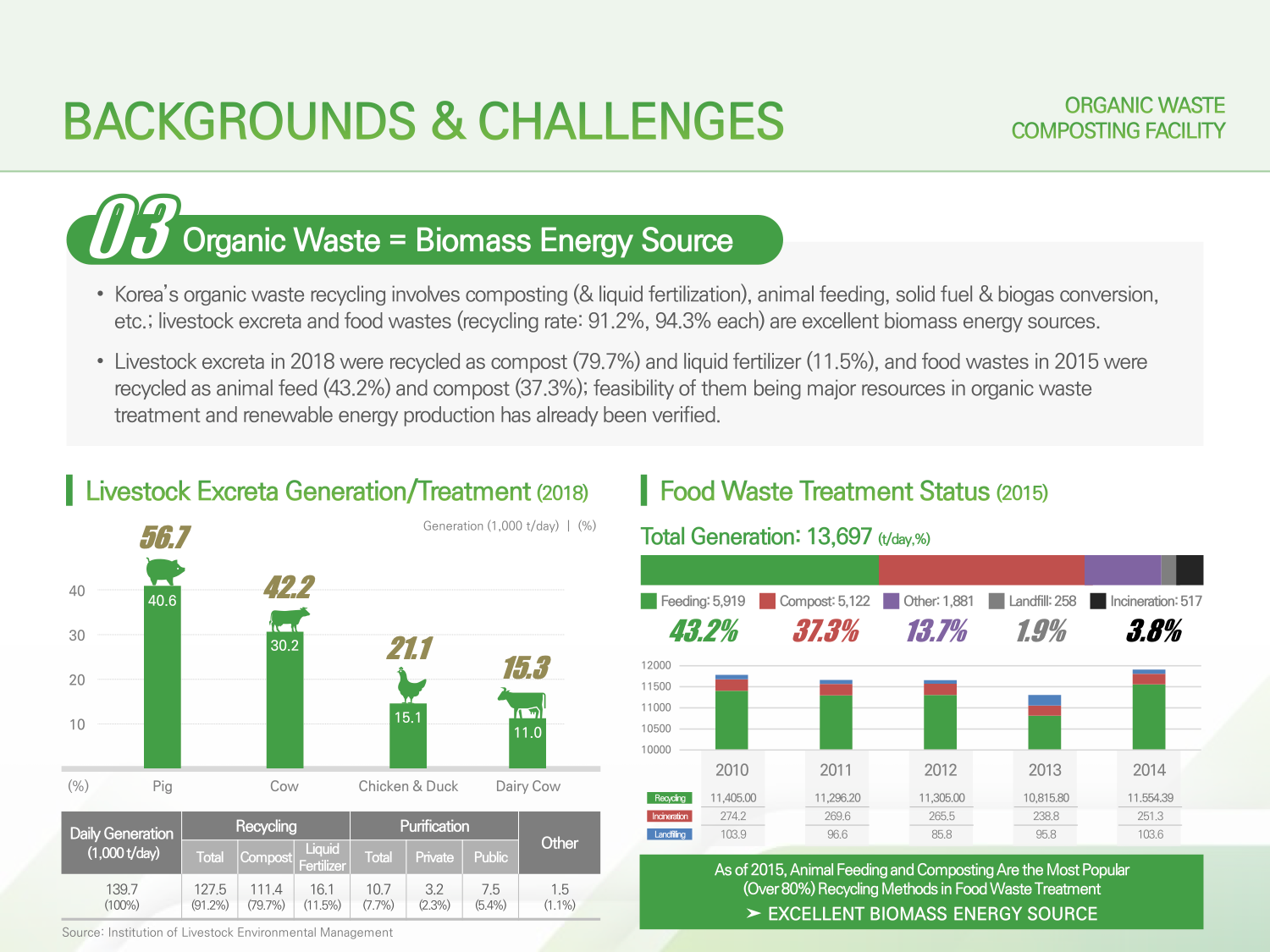
03. 바이오매스 에너지원으로서의 유기성 폐기물
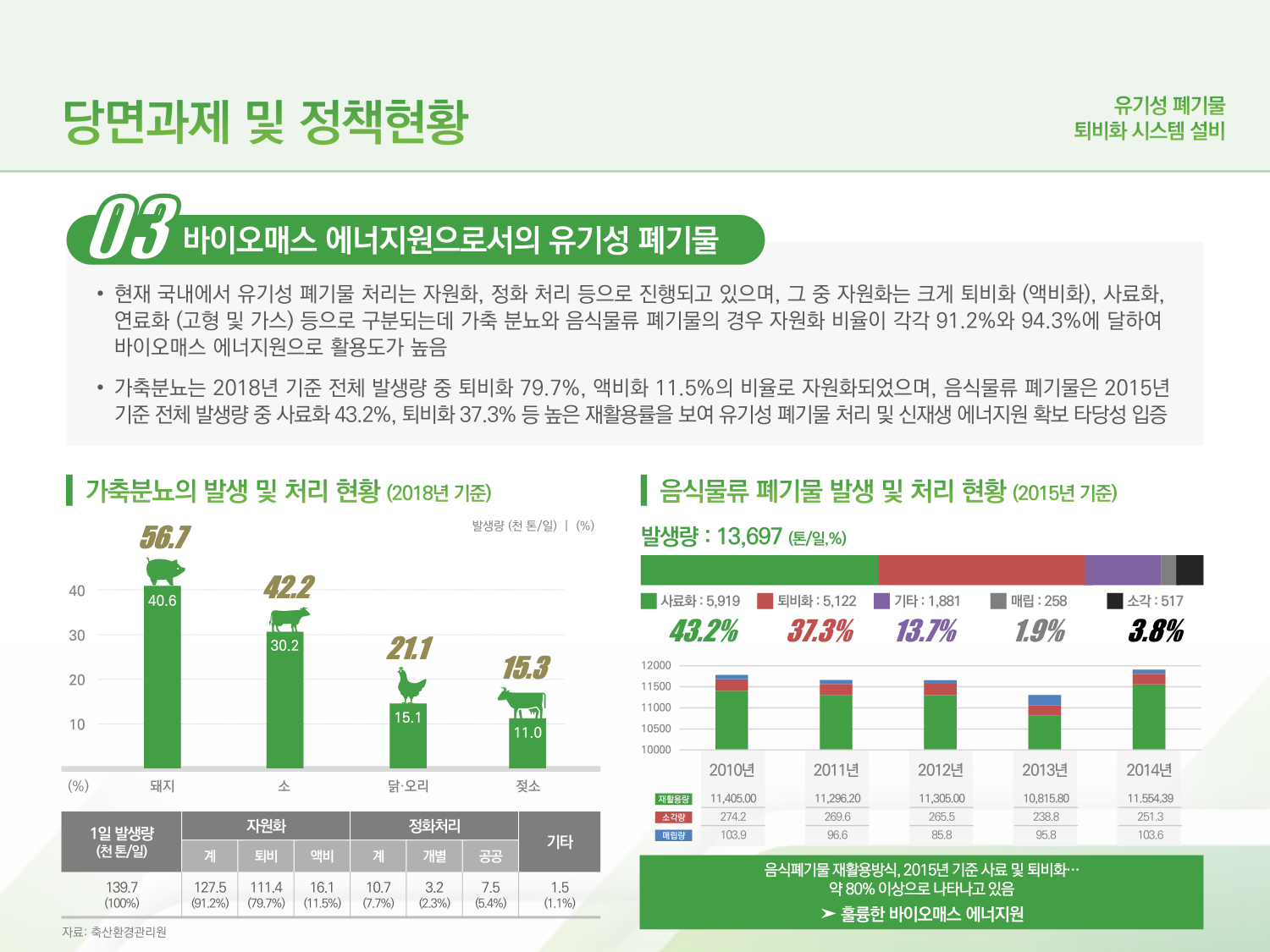
→ 03. Organic Waste = Biomass Energy Source
현재 국내에서 유기성 폐기물 처리는 자원화, 정화 처리 등으로 진행되고 있으며, 그 중 자원화는 크게 퇴비화 (액비화), 사료화, 연료화 (고형 및 가스) 등으로 구분되는데 가축 분뇨와 음식물류 폐기물의 경우 자원화 비율이 각각 91.2%와 94.3%에 달하여 바이오매스 에너지원으로 활용도가 높음
→ Korea’s organic waste recycling involves composting (& liquid fertilization), animal feeding, solid fuel & biogas conversion, etc.; livestock excreta and food wastes (recycling rate: 91.2%, 94.3% each) are excellent biomass energy sources.
가축분뇨는 2018년 기준 전체 발생량 중 퇴비화 79.7%, 액비화 11.5%의 비율로 자원화되었으며, 음식물류 폐기물은 2015년 기준 전체 발생량 중 사료화 43.2%, 퇴비화 37.3% 등 높은 재활용률을 보여 유기성 폐기물 처리 및 신재생 에너지원 확보 타당성 입증
→ Livestock excreta in 2018 were recycled as compost (79.7%) and liquid fertilizer (11.5%), and food wastes in 2015 were recycled as animal feed (43.2%) and compost (37.3%); feasibility of them being major resources in organic waste treatment and renewable energy production has already been verified.

Post a comment